As cyberattacks increase and intensify, the hardening of security measures becomes even more of a necessity, as does compliance with a network of laws and regulations, including SOX compliance.
[ez-toc]

What Is SOX Compliance?
First passed in 2002, the Sarbanes Oxley Act (SOX) requires publicly-traded companies to maintain transparency in financial reporting, preventing fraudulent accounting activities, protecting investors, and improving investor confidence.
The Act includes compliance requirements about external auditors, corporate governance, internal control assessments, and financial disclosures.
SOX IT Compliance Requirements and Reporting
When it comes to IT, SOX compliance requires firms to have policies and procedures in place to prevent, detect, and disclose material cybersecurity risks and incidents. Companies also need to prove that they have data safeguards and procedures in place and that they are operational. This includes quality access management, preventative security measures, and redundant and secure backups.
Additionally, another requirement is that security systems must be able to detect data breaches, and the organization needs a communication plan for notifying leadership and investors of identified breaches. In reporting and during an annual SOX compliance audit, businesses must attest to and provide evidence that these internal controls exist.
One extremely challenging SOX cybersecurity requirement is that businesses are responsible for reporting material cybersecurity risks within four business days after the registrant determines that it has experienced a material cybersecurity incident. This can mean that an organization must disclose a risk or incident before regular reporting or a yearly SOX audit.
Related Content → IT Security and Compliance. What’s the Difference?
SOX in 2023
In both 2011 and 2018, the SEC published guidance for interpreting existing rules in connection with cybersecurity threats and incidents.
However, in 2022, the SEC recommended a proposed rule that would require registrants to provide enhanced disclosures about “cybersecurity incidents and cybersecurity risk management, strategy, and governance.” This rule is part of the Fall 2022 Unified Agenda of Regulatory and Deregulatory Actions released by the Office of Information and Regulatory Affairs. SEC Chair Gary Gensler released a statement in early 2023 acknowledging the Commission’s support of the proposed agenda.
It is significant to note that SOX requires signing officer(s), typically an Executive Officer, to attest that the information in their internal control and financial reports is accurate. They cannot contain any false statements, nor can they omit material information. They also need documentation demonstrating that the organization is SOX compliant. Intentionally or inadvertently generating misleading compliance reports or falsifying information not only leads to noncompliance but can also result in upwards of $5 million in fines and 20 years in prison.
In 2022, the news that Uber’s CISO was convicted of federal charges for failing to disclose a 2016 data breach broke, demonstrating just how severe the consequences of non-compliance can be for individuals as well as companies.
Understanding Risks and Their Impact
How do you know what your material cybersecurity risks and incidents are? How do you know if your firm has experienced a breach?
If your IT team does not have the expertise to continuously analyze risks and understand SOX compliance requirements, they may not see correlations that signify a material risk. Without expert guidance, your firm may miss the context or severity of threats. Businesses may not report minor security incidents deeming them to be immaterial. But what if all these smaller threats and incidents turn out to be a much larger problem? Unable to see the connection between events, an organization could unintentionally omit a material cybersecurity risk in its reporting.
Even worse, failure to evaluate the risk appropriately can lead to security breaches, data loss, lawsuits, and other costly damages.
With such high penalties for failure to appropriately disclose material cybersecurity risks and incidents, it is critical for businesses to implement compliance processes and risk management practices to identify and assess threats across their network. Identified risks need to be assessed and treated appropriately and promptly. This process of assessing and implementing measures to modify risk is known as risk treatment.
To understand the risks in your firm’s environment, it needs continuous network monitoring and the expertise and systems for evaluating and conducting a risk assessment. Partnering with an IT firm with specialized knowledge of the compliance requirements outlined in SOX is ideal to ensure compliance and improve your security posture.
Actively Monitoring for Cybersecurity Threats
There is a difference between performance monitoring and cybersecurity monitoring.
Performance monitoring lets you know if systems are operating efficiently, but it doesn’t tell you what security threats exist or the severity of those risks.
In 2023, the risks from malicious cyberattacks and technology are substantial and are a constant threat. It is no longer acceptable to run occasional cybersecurity scans and assume you are seeing an accurate picture of your overall security posture. Instead, to have a complete understanding of the risks and incidents that occur on your network, you need 24x7x365 activity monitoring.
With a managed detection and response (MDR) platform, a team of security analysts with skills in forensic analysis can identify, evaluate, and provide a response plan to threats and breaches within your network.
SIEM Technology
Without the help of security analysts and security information and event management (SIEM) technology, you may not see the significant link between small risks or incidents.
Security experts use SIEM platforms to correlate and analyze threats. This helps to provide context and severity of risks, which is instrumental in determining materiality.
Keep in mind that you need a security expert to utilize the full benefits of these types of internal security controls.
Meeting SOX Compliance Requirements with Comprehensive Cybersecurity
As mentioned, to maintain SOX compliance, your organization needs to be able to measure the materiality of cybersecurity risks and incidents.
Without the right tools, expertise, and testing, your business could experience a breach causing tremendous financial costs, permanent data loss, or even closure.
Even if your organization is not required to be SOX compliant, implementing internal controls and data protection procedures increases your overall security posture. For a private company or a non-profit, which are not mandated to have SOX compliance programs, creating and monitoring security controls is considered to be a cybersecurity best practice.
Related Content → Evaluate your security readiness with our Cybersecurity Checklist.
To learn more about SOX cybersecurity and compliance solutions, reach out to Coretelligent’s team of experts.



 What is Cyber Hygiene?
What is Cyber Hygiene?

 The growing importance, complexity, and scope of IT, as a whole, has driven many companies to favor
The growing importance, complexity, and scope of IT, as a whole, has driven many companies to favor 



 Humans tend to move on to the next big thing quickly, and with rapidly changing security and regulatory environments, CISOs are no different. We all face new challenges daily, but as we focus on the latest priority in front of us, we must also remember to look back and revisit previous events to ensure we’re practicing hard lessons learned.
Humans tend to move on to the next big thing quickly, and with rapidly changing security and regulatory environments, CISOs are no different. We all face new challenges daily, but as we focus on the latest priority in front of us, we must also remember to look back and revisit previous events to ensure we’re practicing hard lessons learned.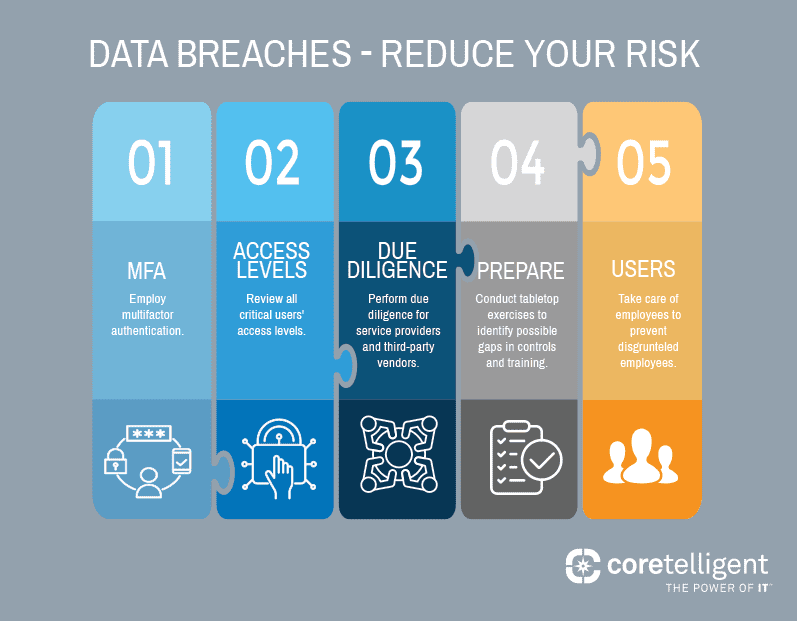
 About Jason
About Jason
 Multifactor Authentication Explained
Multifactor Authentication Explained About Chris
About Chris
