 What is Cyber Hygiene?
What is Cyber Hygiene?
The consistent implementation of cybersecurity best practices to ensure the security and handling of your networks and critical data is what is known as cyber hygiene. Coretelligent will be sharing information and resources to help you fortify your cyber hygiene and keep your business safe from threats.
7 Cyber Hygiene Best Practices
We have put together a list of cybersecurity tips as a quick introduction to persuade your team to assess your firm’s current security readiness from a cyber attack.
-
Double (or triple) up on login protection.
Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) across your organization for all accounts and devices to ensure that only authorized users gain access to your secure data. CISA’s Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) How-to-Guide is a good resource for more information.
-
Shake up your password protocol.
According to the NIST guidance, users should consider using the longest password or passphrase permissible. Encourage end-users to switch up passwords across applications, accounts, and websites. Using unique, strong passwords can make it more difficult for cybercriminals to gain access and protect your organization in the event of a breach.
A password manager and online password generator can be employed to generate and for remembering different, complex passwords. Another solution is to employ SSO to control passwords centrally and avoid user password sprawl across various platforms, which can lead to poor password choices, reuse, and insecure safekeeping.
-
If you connect, you must protect.
Whether it’s a laptop, smartphone, or another networked device, the best defense against viruses and malware attacks is to perform updates on a regular basis to verify that the latest software updates get applied to your software, browser, and operating systems.
A plan that includes the automatic security update is a critical layer of security and part of a multi-layered defense strategy.
-
Don’t get hooked.
Cybercriminals use phishing tactics, hoping to fool their victims. So, if you’re unsure who an email is from—even if the details appear accurate— or if the email looks phishy, do not respond, and do not click on any attachments or suspicious links in emails.
Instead, report the phishing attempt to help your IT team and email provider block other suspicious fake emails before they arrive in your inbox. In addition, the use of random phishing simulations is a valuable exercise to help end-users spot phishing attempts.
-
Beware of social engineering traps.
Many people don’t realize that many of the posts seen on social media asking for seemingly random details are created by criminal networks. They use these posts to gather data that can be mined for potential passwords and other secure information.
For example, posts like, “What car do you wish you still had?” or “Tag your childhood best friend” can be used to help criminals work out the answers to your security questions.
Not only can these tactics impact personal data but are used to target employees in order to gain access to corporate networks. Read CISA’s Social Media Cybersecurity Tip Sheet for more information about good social media and cybersecurity practices.
-
Don’t forget about mobile.
Most connected Internet of Things devices are supported by mobile applications. Mobile devices are often filled with suspicious apps running in the background, or using default permissions users never realized they approved, which are gathering personal information and login credentials without the user being aware.
A robust cybersecurity posture should include a plan for protecting data from employees using compromised mobile devices to access to corporate networks.
-
Stay protected while connected.
Using Virtual Private Network (VPN) for employees remotely connecting is the best way to protect networks. A VPN creates a secure connection that encrypts information so that it’s hidden as it travels. This connection makes it harder for attackers to see and access data.
VPNs are essential when accessing sensitive data like personally identifiable information (like social security numbers) or protected health information, especially when using public wi-fi networks. In today’s hybrid workplace, VPNs are a must to protect against suspicious activity.
From a phishing attack to a ransomware attack, cyber threats are constantly evolving. If you are unsure whether your firm employs good cybersecurity hygiene best practices or not, then it may be time for a security check-up.
Remember, cybercriminals will use any security vulnerabilities they can find to gain access and steal data. You can start with these cybersecurity tips and move on to using our free Cybersecurity Checklist to review your security measures.
Coretelligent is here to help with advice from our cybersecurity experts. Protect your business and learn more about our enhanced managed cybersecurity services designed specifically for small-to-mid-sized companies. Reduce your risk from security incidents – contact us today for help responding to your cybersecurity gaps.


 Multifactor Authentication Explained
Multifactor Authentication Explained About Chris
About Chris

 Improving the operation of your business often starts with consolidation: creating a more cohesive structure that eliminates redundancy and slashes inefficiencies throughout the organization. Business leaders have been focused in this direction for generations, often looking for the smallest advantages that will allow them to outpace the competition. With the renewed focus on cybersecurity, it’s not unusual for businesses to focus more on protecting the security of their organization than attempting to improve operational excellence. What you may not realize is that some of the same initiatives that will help smooth operational hurdles can also provide added levels of cybersecurity. What can be difficult is finding the spaces where you can bring these goals into alignment and create a comprehensive strategy that addresses the holistic needs of the organization and provide proactive cybersecurity support.
Improving the operation of your business often starts with consolidation: creating a more cohesive structure that eliminates redundancy and slashes inefficiencies throughout the organization. Business leaders have been focused in this direction for generations, often looking for the smallest advantages that will allow them to outpace the competition. With the renewed focus on cybersecurity, it’s not unusual for businesses to focus more on protecting the security of their organization than attempting to improve operational excellence. What you may not realize is that some of the same initiatives that will help smooth operational hurdles can also provide added levels of cybersecurity. What can be difficult is finding the spaces where you can bring these goals into alignment and create a comprehensive strategy that addresses the holistic needs of the organization and provide proactive cybersecurity support.
 Even with all of the available technology solutions, one of the biggest challenges you will continue to hear from technical teams is lack of time. Everything from upgrading current platforms to researching new solutions requires dedicated focus, and the ability to shut out all by-the-minute frustrations and do the work required to move your organization into the future. It’s not surprising to find that many business professionals feel as though they are being shut down by IT teams and attempt to “go rogue” — something that would be less likely to happen if IT teams are able to meet their needs more quickly. Outsourced IT solutions is a cost-effective and practical way to solve these challenges.
Even with all of the available technology solutions, one of the biggest challenges you will continue to hear from technical teams is lack of time. Everything from upgrading current platforms to researching new solutions requires dedicated focus, and the ability to shut out all by-the-minute frustrations and do the work required to move your organization into the future. It’s not surprising to find that many business professionals feel as though they are being shut down by IT teams and attempt to “go rogue” — something that would be less likely to happen if IT teams are able to meet their needs more quickly. Outsourced IT solutions is a cost-effective and practical way to solve these challenges.
 President Biden released a
President Biden released a 

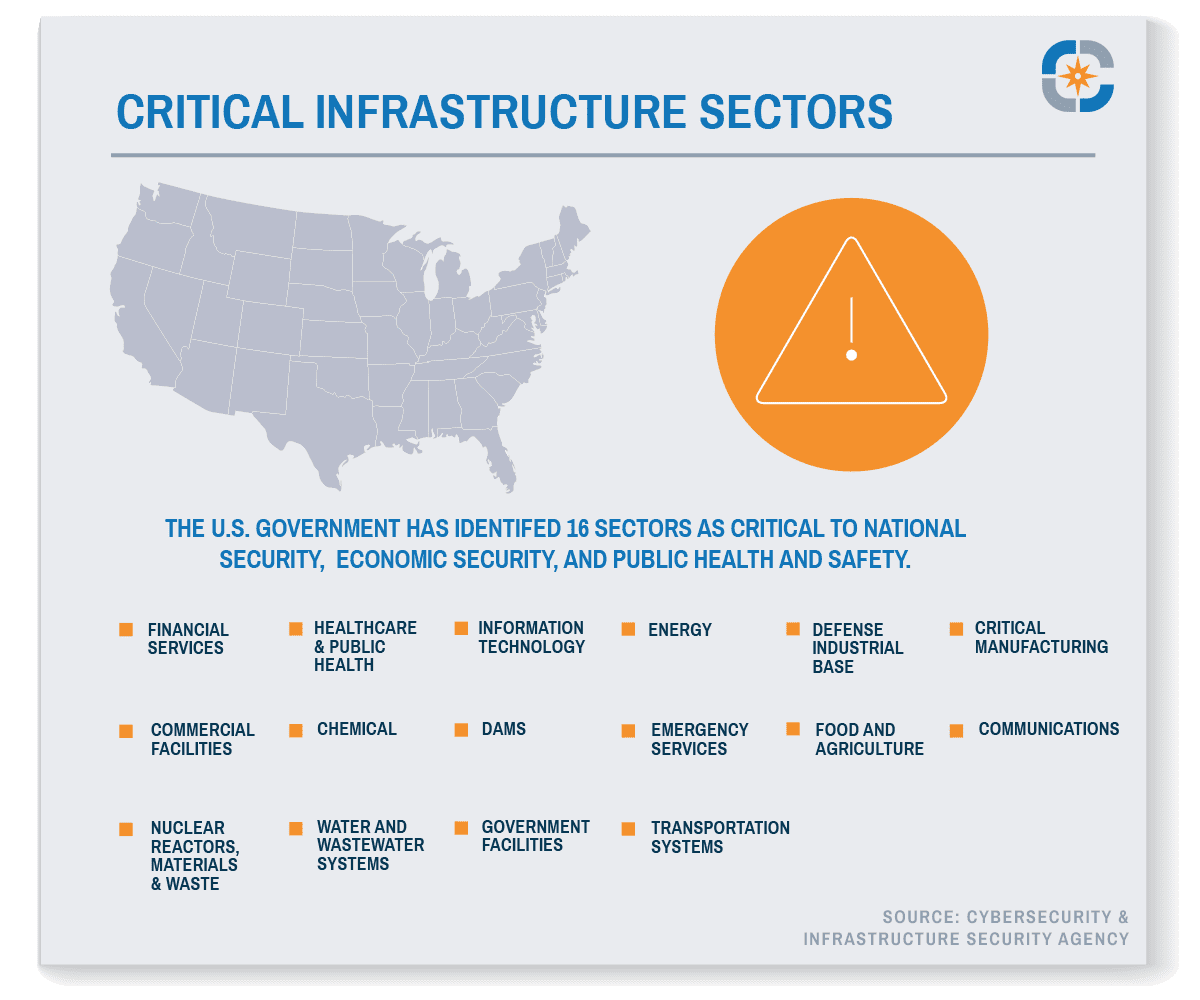
 The Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), the U.S. Intelligence Community, law enforcement, and other agencies recently issued a
The Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), the U.S. Intelligence Community, law enforcement, and other agencies recently issued a 
 Indicates significant changes to regulations for broker-dealers, investment companies, RIA, and other market agents.
Indicates significant changes to regulations for broker-dealers, investment companies, RIA, and other market agents.
