Cyber attacks are becoming increasingly common, and cybercriminals see small to medium-sized businesses as prime targets. The devastating consequences of a cyber attack can be long-lasting and far-reaching, as demonstrated by the chilling story of Expeditors, a logistics company that fell victim to a ransomware attack in 2022 and discovered the true cost of cyber attacks.
[ez-toc]

The Immediate Effects of Expeditors’ Cyber Attack
The ransomware that hit Expeditors left their data and infrastructure at risk, forcing them to halt operations. The immediate effects of the attack were catastrophic, resulting in $47 million in lost revenue, overages, and payouts to customers. Additionally, the company spent $18 million on remediation and recovery efforts, further impacting its bottom line.
Ongoing Impacts: The 2023 iRobot Lawsuit
The fallout from the cyber attack didn’t end with the initial shutdown. In February 2022, Expeditors CIO Christopher J. McClincy said, “The cyber-attack limited our ability to arrange shipments or manage customs and distribution activities, or to perform certain accounting functions, for approximately three weeks after the attack.” Later in the statement, he added, “We continue to navigate residual effects.”
Then in 2023, the company was hit with a lawsuit from iRobot, one of their biggest customers. The lawsuit claims “Expeditors’ own inattentiveness and negligence exposed its systems to attack, and Expeditors lacked and/or failed to implement the necessary business continuity plan to ensure that it could continue providing services to iRobot.”
This legal action added to the ongoing financial impact faced by the company and reignited news stories about the attack—likely impacting the company’s reputation with potential clients, current clients, partners, investors, and other stakeholders.
What’s Your Risk Exposure?
The story of Expeditors should serve as a stark example of the increasing threat that cyber attacks pose to all businesses, but especially to small and mid-sized companies. According to a recent report, 47% of all U.S. businesses suffered some kind of cyber attack in 2022. At the same time, another report found that companies with less than 1,000 employees are three times as likely to be the target of a cyber attack as larger businesses like Expeditors.
Cybersecurity experts say that it’s not if a company will be a target, but when. In fact, a study of penetration testing results found that cybercriminals can penetrate 93 percent of company networks.
Invest in Proactive Measures
Small to medium-sized businesses are seen as easy targets by criminals since they often invest less in cybersecurity and lack security expertise. Cybercriminals understand this and take advantage of these weaknesses, using techniques like phishing, malware, ransomware, and other malicious tactics to gain access to sensitive data or disrupt operations. As a result, it is essential for businesses to invest in robust cybersecurity solutions that can help protect them from cyberattacks.
However, according to the Cyberspace Solarium Commission, many “cybersecurity budgets at U.S. organizations are increasing linearly or flat” when they should be growing in response to the exponential growth of cyber threats.
Best Practices to Mitigate the Risk from Cyber Attacks
Investing in multi-layered cybersecurity is the surest way to keep you and your company out of the headlines. By implementing cybersecurity solutions utilizing best practices, businesses can significantly reduce the likelihood and severity of a cyber incident.
Some key strategies include:
- Investing in robust security solutions: Deploying firewalls, real-time monitoring, and intrusion detection systems can help identify and prevent unauthorized access to your network and data.
- Regularly updating and patching systems: Keeping software and systems up to date ensures protection against known vulnerabilities, making it more difficult for cyber criminals to exploit your systems.
- Implementing strong access controls: Restricting access to sensitive data and systems through multi-factor authentication and the principle of least privilege minimizes the risk of unauthorized access.
- Educating employees on cybersecurity best practices: Regular training on topics such as recognizing phishing emails and creating strong passwords can reduce the risk of employees inadvertently compromising your network.
- Developing a comprehensive incident response plan: A well-defined incident response plan outlines the steps to be taken during a breach, including containing the incident, assessing the damage, and recovering from the attack.
By learning from the Expeditors case study and prioritizing cybersecurity, businesses can better protect themselves from the devastating consequences of cyber attacks and ensure long-term success. Protect your business from cyber threats with a comprehensive security risk assessment that can help identify any areas of vulnerability and provide guidance on best practices to shield your organization.






 Humans tend to move on to the next big thing quickly, and with rapidly changing security and regulatory environments, CISOs are no different. We all face new challenges daily, but as we focus on the latest priority in front of us, we must also remember to look back and revisit previous events to ensure we’re practicing hard lessons learned.
Humans tend to move on to the next big thing quickly, and with rapidly changing security and regulatory environments, CISOs are no different. We all face new challenges daily, but as we focus on the latest priority in front of us, we must also remember to look back and revisit previous events to ensure we’re practicing hard lessons learned.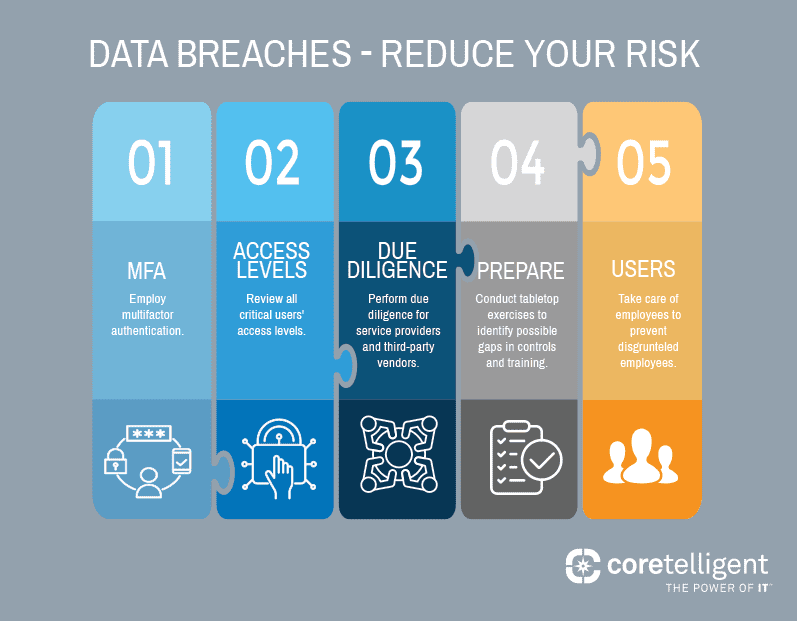
 About Jason
About Jason


