As we look back on 2023, the surge in cyber attacks has emerged as a formidable challenge, particularly for small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs). With limited resources and often less sophisticated security measures, SMBs have become attractive targets for cybercriminals.
On average, these incidents cost SMBs an alarming $25,000, a significant financial strain that can jeopardize their survival. The rise in cybercrime is not just a statistic; it’s a call for SMBs to fortify their digital defenses.
Understanding the Current Cybersecurity Landscape
Common Types of Cyber Attacks: Among the myriad of cyber threats, certain types are more prevalent in targeting SMBs. Malware and ransomware, especially, stand out, with 18% of attacks on small businesses being malware-related.
The Financial Burden: The financial implications of these attacks are substantial. The average cost of a data breach for SMBs has escalated to $4.35 million, the highest on record, and the recovery from a ransomware attack can cost nearly as much.
The Prolonged Response Time: Another critical aspect of the current landscape is the time it takes to identify and contain a breach. On average, it took about 277 days, approximately nine months, to identify and contain a breach in 2022. This prolonged response time can exacerbate the damage caused by a breach, both financially and in terms of customer trust.
The Role of Human Error: It’s important to note that human error plays a significant role in the vulnerability of SMBs to cyber attacks. A significant portion of breaches, 43%, involve insider threats, either intentional or unintentional. Additionally, the fact that 94% of malware is delivered via email highlights the need for continuous employee education and vigilant email security practices .
The Impact of Remote Work: The shift to remote work has introduced additional complexities. Remote work not only increases the attack surface for cybercriminals but also leads to higher costs per breach. Distractions at home contribute to employees falling prey to phishing scams, and breaches in remote work settings take longer to contain.
The cybersecurity landscape for SMBs is characterized by a high frequency of targeted attacks, significant financial implications, and extended breach identification times. These challenges are compounded by factors such as human error and the increasing prevalence of remote work. Understanding these dynamics is the first step for SMBs in developing a strong cybersecurity strategy that can withstand the rising tide of cyber threats.
The Impact of Cyber Attacks on SMBs
Cyber attacks on small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) have wide-ranging and serious consequences, extending beyond immediate financial losses:
- Financial Strain: The average cost of a data breach for SMBs is around $4.35 million, and recovering from a ransomware attack can cost nearly $2 million. These costs can significantly strain an SMB’s finances, sometimes leading to bankruptcy.
- Operational Disruptions: Cyber attacks can cause extended operational downtimes due to the average breach detection and containment time of 277 days. This downtime disrupts business continuity, affects productivity, and can result in the loss of clients.
- Reputational Damage: A security breach can severely damage an SMB’s reputation, leading to a loss of customer trust and potentially long-term business relationships.
- Legal and Regulatory Consequences: Breaches can lead to legal and regulatory issues, especially if sensitive customer data is compromised, attracting fines and legal actions.
- Psychological Impact: The stress and anxiety associated with a cyber attack affect both business owners and employees, impacting morale and job security.
- Strategic Setbacks: Resources diverted to manage and recover from an attack can delay or cancel business growth or innovation initiatives.
- Increased Cybersecurity Costs: Post-attack, businesses often face increased spending on cybersecurity measures, adding to financial burdens.
The multifaceted impact of cyber attacks underscores the necessity for SMBs to prioritize robust cybersecurity measures to safeguard their operations, finances, and reputation.
Key Vulnerabilities in SMBs
Strategies for Enhanced Cybersecurity
- Regular Updates and Patch Management: Ensure devices are configured for automatic updates and regularly check for installed updates.
- Strong Password Policies: Implement policies for complex, unique passwords, and encourage using password managers.
- Access Control & Multi-Factor Authentication: Employ strong access control and multi-factor authentication to prevent unauthorized access.
- Data Backup and Recovery: Maintain reliable data backups and test backup procedures regularly, especially against ransomware threats.
- Firewall and Endpoint Detection: Implement firewall security and endpoint detection systems to block suspicious traffic and identify unusual activities.
- Data Encryption: Encrypt sensitive data both at rest and in transit.
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct audits to evaluate cybersecurity controls and address vulnerabilities.
- Incident Response Plan: Develop and regularly rehearse a detailed incident response plan.
- Employee Education and Awareness: Train employees on cybersecurity best practices, including recognizing phishing attempts.
Professional Cybersecurity Solutions
Consider solutions like CoreArmor and CoreComply, which provide advanced threat detection, managed security services, and strategic planning tailored to SMB needs. CoreArmor, for example, bundles essential cybersecurity services into a comprehensive package, covering real-time monitoring, incident response, penetration testing, vulnerability scanning, and user awareness training. While CoreComply, strengthens compliance operations, aligning them with business processes and helping to identify and close gaps in current practices.
Implementing these strategies and leveraging professional solutions like CoreArmor and CoreComply can significantly enhance an SMB’s cybersecurity posture, protecting against a broad spectrum of cyber threats and vulnerabilities.
What You Can Do
In the face of evolving cyber threats, small and medium-sized businesses must prioritize robust cybersecurity. Coretelligent offers tailored solutions like CoreArmor and CoreComply, blending advanced threat detection, strategic planning, and compliance management. Protect your business with our comprehensive cybersecurity services.
If you’re interested in learning what you can do to fortify your business’s defenses, watch our recent webinar, where we bring together a panel of experts, including an FBI special agent that that works on cybercrime cases, a cyber insurance specialist, and our very own team as they dive into trends, tips, and valuable insights you can use to understand the various threats at play.













 Humans tend to move on to the next big thing quickly, and with rapidly changing security and regulatory environments, CISOs are no different. We all face new challenges daily, but as we focus on the latest priority in front of us, we must also remember to look back and revisit previous events to ensure we’re practicing hard lessons learned.
Humans tend to move on to the next big thing quickly, and with rapidly changing security and regulatory environments, CISOs are no different. We all face new challenges daily, but as we focus on the latest priority in front of us, we must also remember to look back and revisit previous events to ensure we’re practicing hard lessons learned.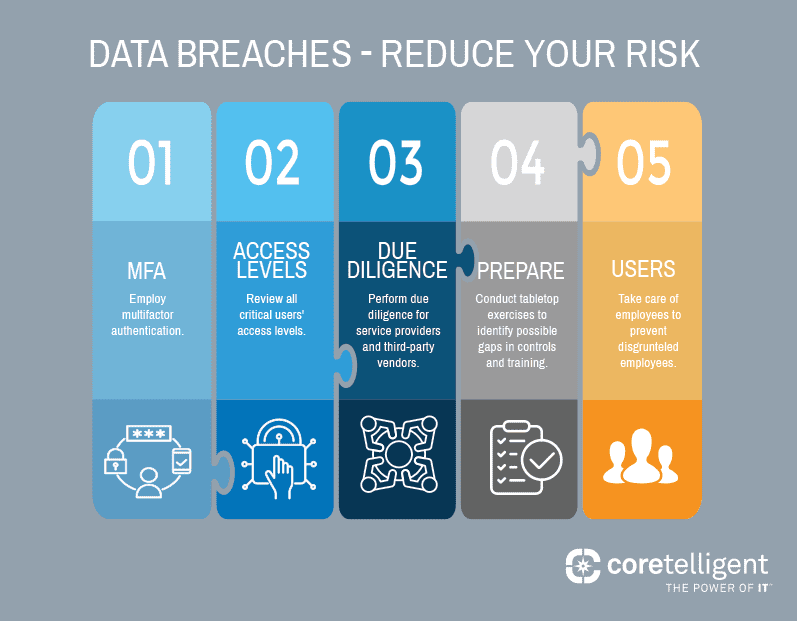
 About Jason
About Jason
