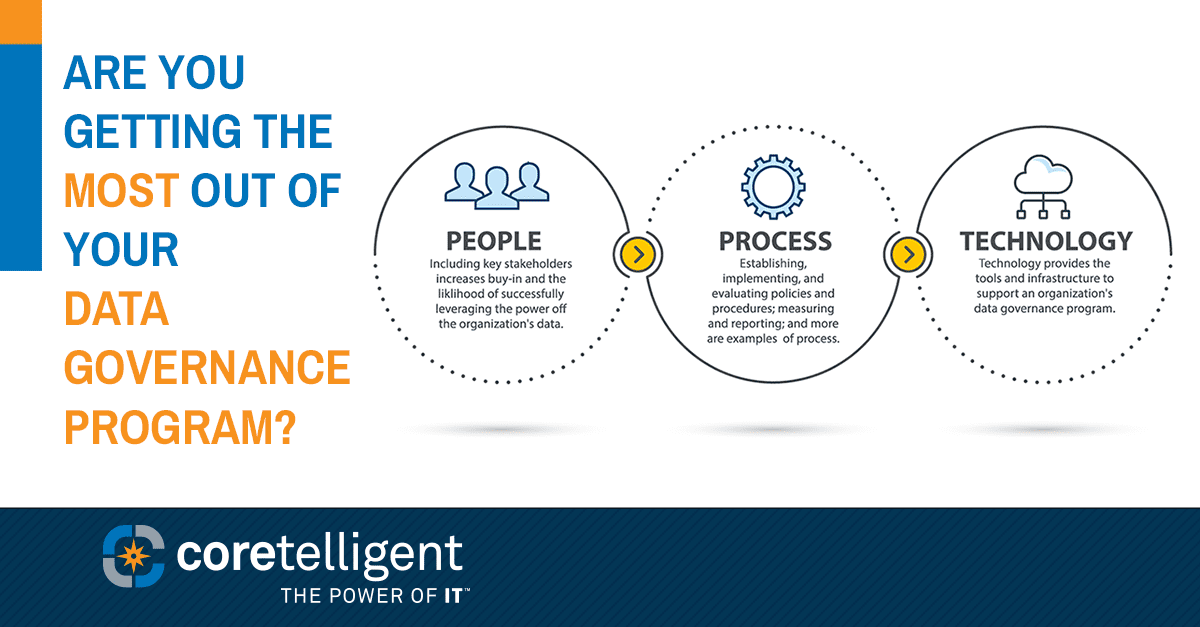
As business operations become increasingly complex and interconnected, third-party risk management (TPRM) is no longer optional.

You Are Only as Safe as Your Vendors
Companies rely heavily on third-party vendors, suppliers, and partners to perform critical functions in today’s business landscape. A recent study reports that 71% of organizations have seen their third-party networks increase in the last three years. While these relationships can drive growth and efficiency, they also introduce potential risks that need to be carefully managed.
What is Third-Party Risk Management?
Third-Party Risk Management refers to the strategies and processes used to identify, assess, and mitigate risks from doing business with third-party entities. These external entities can include suppliers, vendors, contractors, affiliates, or any other organization your business interacts with.
The risks associated with third-party relationships can be varied, ranging from operational and financial risks to reputational and legal risks. For instance, if a vendor suffers a data breach, your company could be exposed to operational risks, financial losses, regulatory penalties, reputational damage, lawsuits, and even dissolution.
The Importance of TPRM in Today’s Business Environment
In recent years, high-profile incidents have highlighted the significant risks that third-party relationships can pose. 59% of organizations reported experiencing a data breach caused by a third party, with 54% reporting breaches within the last 12 months.
The consequences of not effectively managing third-party risks can be severe, from data breaches involving third-party vendors to operational disruptions caused by supplier failures.
Furthermore, regulatory bodies are increasingly focusing on third-party risk management. Data regulations like HIPAA, SEC, CCPA, and the New York Shield Act, among others, include requirements for data protection that require robust third-party risk management practices in place.
Implementing Effective TPRM: Key Steps for Business Executives
Effective third-party risk management requires a strategic and proactive approach. Here are some key steps that business executives should consider:
- Conduct Thorough Due Diligence: Before engaging with a third party, conduct a comprehensive due diligence process to understand their capabilities, reliability, and track record. This process includes assessing their financial stability, compliance status, and cybersecurity measures.
- Establish Clear Contracts: Ensure your contracts with third parties clearly outline roles, responsibilities, and expectations, including defining performance metrics, data protection requirements, and penalties for non-compliance.
- Regularly Monitor Third Parties: Continuous monitoring of your third parties is crucial for detecting and responding to potential risks promptly. Implement regular audits, performance reviews, and compliance checks.
- Develop a Response Plan: Have a contingency plan in place to respond to incidents involving third parties. This plan should include steps for mitigating damage, notifying stakeholders, and resolving the issue.
- Leverage Technology: Utilize technology solutions to streamline your TPRM processes. This can include a solution that will automate due diligence, monitor third-party performance, alert you to potential risks, as well as strategic guidance.
- Conduct a Risk Assessment: Regularly review your third-party relationships to identify any potential risks and address them promptly.
The reality of today’s digital ecosystem means that third-party risk management is a critical aspect of modern business strategy. By understanding the potential risks and implementing effective solutions, business executives can protect their organizations, enhance operational resilience, and drive sustainable growth.
DOWNLOAD THE FREE GUIDE → Comprehensive Guide to Third-Party Risk Management










 About Chris
About Chris

 Disasters and cyber-attacks happen, but data loss does not have to be inevitable. Data loss can be
Disasters and cyber-attacks happen, but data loss does not have to be inevitable. Data loss can be