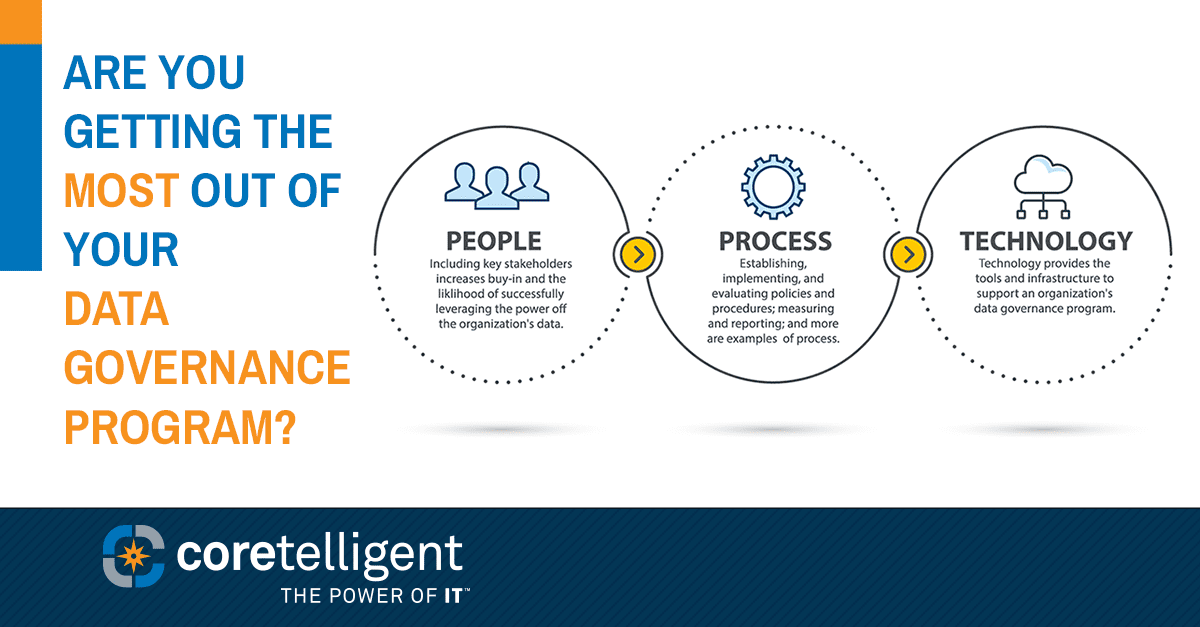
Last year the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) voted to implement new and amended SEC RIA requirements to the Advisers Act of 1940 for cybersecurity risk management for registered investment advisers (RIAs) and funds.
Is your firm ready?
[ez-toc]

The proposed SEC rule changes would oblige RIA firms to develop and implement written policies and procedures to reduce cybersecurity risks that could harm clients and fund investors. The proposed regulations would also force advisers to report cybersecurity incidents like data breaches involving client information to the SEC.
Additionally, the proposed changes call for publicly disclosing cybersecurity risks and significant incidents from the last two fiscal years in their marketing materials and registration statements.
“The proposed rules and amendments are designed to enhance cybersecurity preparedness and could improve investor confidence in the resiliency of advisers and funds against cybersecurity threats and attacks,” said SEC Chair Gary Gensler.
While comments initially closed in April 2022, comments were reopened on March 15, 2023. Once comments are fully closed, the finalized rules will most likely become effective later in 2023. We will be providing future updates once the final regulations are published.
What do the New SEC RIA Cybersecurity Requirements Entail?
The four significant proposed changes include the following:
- The proposal consists of new rule 206(4)-9 under the Advisers Act and new rule 38a-2 under the Investment Company Act. In addition, the proposed cybersecurity risk management rules require public companies to adopt and implement policies and procedures for identifying, assessing, and mitigating cyber risks.
- The proposal also includes a reporting requirement under new rule 204-6 mandating companies report significant cybersecurity incidents affecting the adviser, its fund, or private fund clients.
- The updated rules include changes to Form ADV Part 2A requiring advisers and funds to publicly disclose cybersecurity risks and significant cybersecurity incidents that occurred in the last two fiscal years in their brochures and registration statements.
- The proposal also includes new recordkeeping requirements under the Advisers Act and Investment Company Act Rule 204-2 to improve the availability of cybersecurity-related information and help facilitate the Commission’s inspection and enforcement capabilities.
RELATED CONTENT → Security vs. Compliance: Differences & Similarities
What Can You Do to Prepare for RIA Cybersecurity Enforcement?
Here are some expert tips on being ready for enforcement when the changes go into effect later this year.
- Develop and Implement Policies and Procedures
RIAs and funds must create comprehensive cybersecurity policies and procedures to mitigate cybersecurity risks per the proposed rules. Keep in mind that these policies and procedures must be both compliant and actionable.
- Conduct a Risk Assessment
Evaluate cybersecurity risks by identifying, categorizing, and prioritizing cybersecurity risks related to your systems and operations. By conducting an effective risk assessment, you’ll have the necessary information to develop compliant policies and procedures to combat potential cybersecurity risks.
- Prepare for Disclosure Obligations
When it comes to disclosures associated with cybersecurity risks or incidents, develop procedures for clear, accurate, and timely disclosures to the SEC, clients, investors, and other market participants.
- Continuity Planning
In the event of a cybersecurity incident, you must be able to maintain system operations. So, test your incident response and business continuity plans through tabletop exercises to ensure compliance with the requirements.
- Reporting and Documentation
Employing a governance, risk, and compliance (GRC) solution will ensure you have well-documented evidence that your cybersecurity program is compliant.
In addition to ensuring that your firm will align with the changes, these suggestions are also considered best practices for mitigating the risks from data breaches and other cyber attacks. Following these and other practices makes good sense whether your firm is required to or not.
To learn more about GRC, download our free guide → Understanding Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance for Financial Services.
By employing these practices, you’ll be ready for any forthcoming changes to cybersecurity regulations and well-protected against potential security threats. One solution for preparing now or later is to work with an experienced and knowledgeable IT service provider. An IT partner experienced with RIA firms, and one employing robust cybersecurity and compliance solutions can reduce the time and resources it takes to comply with and implement these and other cybersecurity compliance standards.




 What is Cyber Hygiene?
What is Cyber Hygiene?


 Disasters and cyber-attacks happen, but data loss does not have to be inevitable. Data loss can be
Disasters and cyber-attacks happen, but data loss does not have to be inevitable. Data loss can be